Barcode and DMC code reading with industrial cameras and image processing software
This article describes how to use the most affordable machine vision camera solution to read barcodes and DMC codes (Datamatrix codes). Furthermore, we explain the distinction between DMC codes and barcodes by going over their advantages and disadvantages. We also include a formula to assist you in determining the necessary resolution, along with useful examples for reading DMC and barcodes.
Barcodes vs. DMC codes
DMC codes are preferable to barcodes when it comes to code reading with industrial machine vision cameras. Lower resolution cameras can read DMC codes with the same field of view as barcodes. Therefore, you can use less expensive cameras to read DMC codes. This implies that you can examine a larger field of view using DMC codes for the same hardware and cost.
DMC code, also known as a datamatrix, is a matrix of dots. Module size is used to specify the dot size. These dots are easier for machine vision algorithms to read than the extremely thin lines used in barcodes.
The ratio of the smallest detail's size to the field of view area we wish to examine in a single frame or image determines the necessary resolution.
Additionally, DMC codes are significantly smaller than barcodes, which lowers the necessary label size. This is an illustration of a DMC code label and a BARCODE label that have the exact same information.

Rolling versus global shutter industrial cameras
The industrial camera's price is significantly influenced by the type of shutter for resolutions higher than 1.6MP. A global shutter can be used when there is movement, whereas a rolling shutter can only be used when the camera and the object are motionless. Check out our knowledge center's in-depth article on shutter types for more specific details on the distinctions between rolling and global shutters or ask your question in the form below!
Questions or support?
As an actual example, we require a 12MP camera resolution. The price comparison of a rolling shutter vs. global shutter camera system is shown below:
12MP Rolling shutter with lens: MER2-1220-32U3M + LCM-10MP-12MM-F2.8-1.5-ND1 = from $500
12 MP Global shutter with lens: ME2P-1230-23U3C + LCM-10MP-16MM-F1.6-1.3-ND1 = from $1600
Please be aware that not every type of shutter is offered in the same resolution. With the exception of the 12MP cameras, it is therefore impossible to compare the same resolution cameras in the price example above.
Calculating the required camera resolution for barcode
We must know the size of the field of view and the width of the thinnest line of the barcode we wish to see in order to compute the resolution required to inspect barcode labels.
We can either narrow the field of view or make the barcode's thinnest line larger in order to lower the required resolution.
Calculating the required camera resolution for DMC code
We must determine the size of the field of view and the smallest dot or square (module size) in the datamatrix in order to determine the resolution required to inspect DMC code labels.
We can either decrease the field of view or increase the DMC code's module size in order to lower the required resolution.
Minimum resolution vs. recommended resolution for code reading
For reliable, steady DMC code and barcode reading, resolution is essential. We compute the system configuration in two scenarios in this example: minimum resolution and recommended resolution.
A minimum of 1.5 pixels per linewidth (for barcodes) or 1.5 pixels per dot (for DMC codes) is what we require for minimum resolution. If the label quality, light, geometry, and other parameters are all at their ideal levels, or if you take several pictures of the same code. This might operate steadily.
At least two pixels per linewidth (for barcodes) or two pixels per dot (DMC) is the recommended resolution. Three pixels is the ideal answer. The camera resolution is higher than necessary if there are more pixels per linewidth or dot. There will be a higher setup cost overall. On the other hand, reading DMC codes and barcodes will be simpler, quicker, better, and more stable with more pixels.
Formula for resolution calculation
You can use the following formula to determine the resolution:
Camera resolution = Field of view / system resolution
System Resolution = (Thinnest line or module size) / (minimum or recommended resolution per thinnest line or module size).
Ex: Which camera do I need to detect a barcode with a thinnest line of 1mm in a field of view of 1000*600mm. We go for the recommended resolution.
System Resolution = 1mm/2pixels= 0.5 mm/pixel
Horizontal Camera Resolution = 1000 mm (horizontal FOV) / 0.5mm (system resolution) = 2000pixels
Vertical camera Resolution = 600 mm (vertical FOV) / 0.5mm (system resolution) = 1200pixels
Our system will need a camera with a resolution of at least 2000*1200 pixels = 2.4MP camera.
We would suggest a 6MP rolling shutter camera if the object is motionless. We advise the 3MP global shutter camera if the object is moving.
The importance of image processing software in machine vision barcode / DMC label reading
The choice of software is essential for reading barcodes and DMC codes. The ability of the system to read and recognize codes is essential. In general, codes can be recognized, read, and decoded more easily the better the software algorithms.
The power of Zebra Aurora Vision software
Aurora Vision Image processing software
Selecting the right software is crucial for decoding DMC and barcodes. It is imperative that the system be able to read and recognize codes. In general, the more advanced the software algorithms are, the easier it is to recognize, read, and decode codes.
The tools are incredibly strong and quick. In every test we conducted, we outperformed customers using open-source code reading algorithms in terms of reading success ratio on challenging images. Particularly in situations with poor lighting or low resolution (such as reflections).
Here's an example of how to use Aurora Vision Studio to read barcodes:
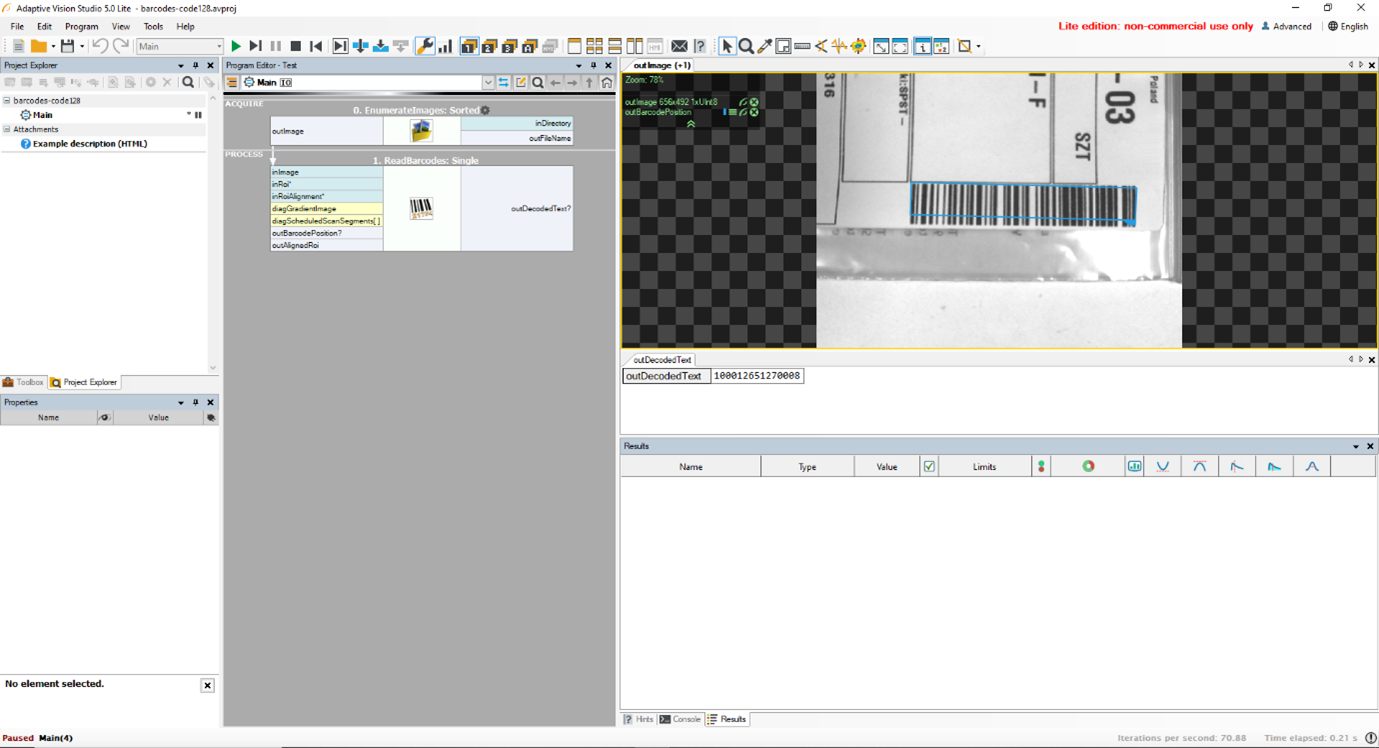
Code reading application in practice
Reducing the field of view will, as previously mentioned, lower the necessary camera resolution. One clever way to set up a system is to move the cameras or the products to capture multiple images if the field of view is very wide in relation to its height.
For example, instead of using five cameras, you could move one camera on a trolley and take five pictures of 2 by 2 meters, if your field of view is 10 by 2 meters and you want to detect barcodes or DMC.
Line scan cameras vs area scan cameras for code reading
What makes Line scan cameras different from Area scan cameras in terms of barcode detection is a question we get from our customers all the time.
When an object passes under the sensor of a line scan camera, an image is reconstructed line-by-line in software for inspection. When moving the products beneath the camera with a conveyor belt, line scan cameras are the best option. The timing of each pixel line capture for line scan cameras is critical, as it varies based on the passing object's speed. Encoders are used frequently. The cost of a line scan camera is high, and encoders are required to provide a stable solution.
Installing area-scan cameras is simpler, more affordable, and offers greater flexibility. They are able to read DMC codes and barcodes in radically different settings. Consequently, an area scan camera is used in more than 95% of applications for reading barcodes or DMC codes.
Conclusion for DMC and barcode reading
DMC codes are the most affordable option if you're looking for a code reading solution. Low-resolution cameras are less expensive than high-resolution cameras, and they can still read the datamatrix. If you would like to read barcodes and reduce the cost of your DMC code reading solution, we suggest using a rolling shutter instead of a global shutter camera, as they are less expensive.
Additionally, you can decrease the field of view or increase the size of the thinnest line or dot to reduce the required resolution. Using multiple cameras to cover the entire field of view is another way to reduce the field of view.
Any other questions about barcode or data matrix code reading?
Please get in touch with us if you have any additional queries concerning code reading. We are always pleased to assist you.
Do you think the articles in our knowledge center are useful? We will post new articles on LinkedIn as soon as they are released, so be sure to follow GeT Cameras there.


